Buddhism is a religion and philosophy originating in India with the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, who is commonly known as the Buddha. Buddhism spread throughout Asia and became a major world religion. Over time, Buddhism has divided into many different schools and sects.
Buddhism originated in India in the 6th century BCE. The founder of Buddhism was Siddhartha Gautama, a prince who renounced his royal heritage to become a monk. After years of study and meditation, Gautama attained Nirvana, or enlightenment. He then spent the rest of his life teaching others the path to Nirvana.
How did Buddhism begin?
When Gautama Buddha passed away around 483 BC, his followers began to organize a religious movement based on his teachings. This movement would eventually develop into Buddhism. In the 3rd century BC, Ashoka the Great, the Mauryan Indian emperor, made Buddhism the state religion of India.
Buddhism is one of the world’s most popular religions with an estimated 350 million followers. It is based on the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, who lived in the area that is now Nepal around the 5th century BCE. Buddhism teaches that life is a cycle of suffering and rebirth, that we can be liberated from this cycle by following the Eightfold Path, and that Nirvana is the ultimate goal. Buddhists seek to live in harmony with all beings, and they believe that everyone has the potential to attain Nirvana.
Where did Buddhism originate
Buddhism is a religion that originated in Ancient India, in and around the ancient Kingdom of Magadha. It is based on the teachings of the ascetic Siddhārtha Gautama. The religion evolved as it spread from the northeastern region of the Indian subcontinent throughout Central, East, and Southeast Asia.
Buddhism is a religion that was founded in the late 6th century BCE by Siddhartha Gautama. It is an important religion in many Asian countries. Buddhism teaches that the way to end suffering is to live a life of compassion and wisdom.
Who created the religion of Buddhism?
Buddha was a spiritual leader and founder of Buddhism who lived in the 6th-4th century BCE. He was born in Lumbini, near Kapilavastu, in the Shakya republic of the Kosala kingdom. Buddha’s teachings emphasised personal spiritual development, morality, and meditation. He is known for his Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, which outline the path to Nirvana, or enlightenment. Buddha died in Kusinara, in the Malla republic of the Magadha kingdom.
Siddhartha Gautama, the founder of Buddhism, was born circa 563 BCE into a wealthy family. Gautama rejected his life of riches and embraced a lifestyle of asceticism, or extreme self-discipline. After 49 consecutive days of meditation, Gautama became the Buddha, or “enlightened one”.
Buddhism teaches that life is a cycle of birth, death, and rebirth. The goal of Buddhism is to break out of this cycle and attain Nirvana, or a state of perfect peace and bliss. Nirvana is attained through the practice of the Eightfold Path, which includes ethical conduct, wisdom, and meditation.
Buddhism is a nontheistic religion, meaning that it does not believe in a personal god. Instead, Buddhists focus on their own individual spiritual journey. Buddhism has a long and rich history, and it has had a significant impact on the cultures of Asia.
What are the 3 main Buddhist beliefs?
Buddhism is a religion that is based on the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama. The main principles of this belief system are karma, rebirth, and impermanence.
Karma is the belief that our actions have consequences, both in this life and in future lives. rebirth is the belief that after we die, we are reborn into another body. impermanence is the belief that everything is constantly changing and nothing lasts forever.
These beliefs can be helpful in understanding the Buddhist perspective on life and death.
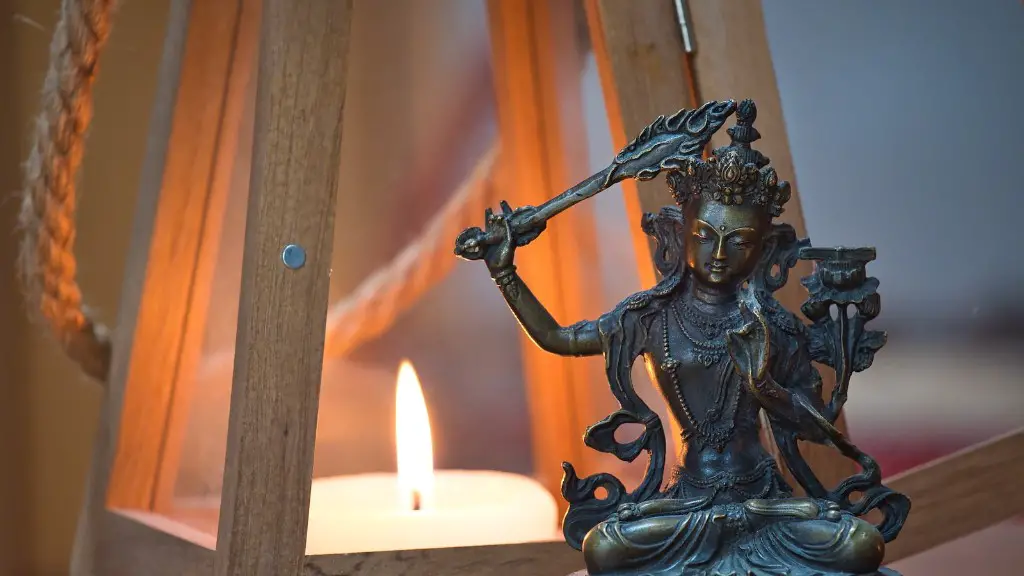
Vajrapāṇi, Mañjuśrī and Avalokiteśvara are three of the most important Buddhist deities. Each represents a different aspect of the Buddha’s teachings and each has a different role to play in the lives of Buddhist followers.
Vajrapāṇi is the Buddha of Power and is often depicted holding a vajra, or Thunderbolt, in his hand. He represents the power of the Buddha’s teachings and the ability to overcome all obstacles.
Mañjuśrī is the Buddha of Wisdom and is often depicted holding a sword in his hand. He represents the wisdom of the Buddha’s teachings and the ability to cut through ignorance and delusions.
Avalokiteśvara is the Buddha of Compassion and is often depicted holding a lotus flower in his hand. He represents the compassion of the Buddha’s teachings and the ability to help all beings find peace and liberation.
What is the oldest religion
Sanātana Dharma is a term used to refer to the Hindu religious tradition. The word Hindu is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as Sanātana Dharma (Sanskrit: सनातन धर्म, lit.
Buddhism is a religion that does not believe in a creator God. It was founded by Siddhartha Gautama, also known as Buddha. Siddhartha Gautama was once a Hindu prince.
What is the Buddhist god name?
Bodhisattvas who are seen as powerful and highly advanced are highly venerated in this tradition. In the East Asian Buddhist traditions, which are mainly Mahayana, major bodhisattvas include: Guanyin, Maitreya, Samantabhadra, Manjushri, Ksitigarbha, Mahasthamaprapta, Vajrapani and Akasagarbha.
Most scholars believe that Buddhism had no influence on Christianity. Paula Fredriksen stated that no serious scholarly work has placed the origins of Christianity outside the backdrop of 1st century Palestinian Judaism.
What is Buddhism’s holy book called
The Tripitaka (Pali: “Three Baskets”) is the complete canon of the Theravada branch of Buddhism. It consists of the Vinaya Pitaka (monastic rules), the Sutta Pitaka (Buddhist sermons), and the Abhidhamma Pitaka (philosophical/psychological analyses).
The Tripitaka was first written down in Pali, the sacred language of Theravada Buddhism, around the 1st century BCE. It was subsequently translated into a number of other languages, including Sanskrit, Chinese, and Tibetan.
The Tripitaka is the most complete and authoritative record of the teachings of the Buddha. It is essential reading for all who wish to understand the core teachings of Theravada Buddhism.
Buddhism began as an offshoot of Hinduism, with its founder, Siddhartha Gautama, born in what is now Nepal in 563 BCE. Gautama’s lifetime saw the rise of the Maurya Empire in India, which ushered in a period of relative peace and prosperity. This allowed for the spread of Buddhism beyond its South Asian origins. While early Buddhism retained many of the beliefs and practices of Hinduism, it also departed in several significant ways. For instance, the Buddha taught that there is no soul, that the world is characterized by suffering, and that salvation lies in escaping the cycle of rebirth. These ideas were not part of mainstream Hindu thought, and helped to set Buddhism apart as its own distinct religion.
Did Buddhism or Christianity start first?
Buddhism is one of the oldest religions in the world, with its origins dating back to the 6th century BCE. Buddhism is based on the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, who is also known as the Buddha. Buddhism teaches that the way to achieve Nirvana, or spiritual enlightenment, is through the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path. Christianity, on the other hand, is a monotheistic religion that is based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christianity teaches that there is only one way to achieve salvation, and that is through faith in Jesus Christ.
In the first understanding the Buddha (represented in English with a capital B) was an unusual human born into a royal family in ancient India in the sixth or fifth century BCE. He is said to have experienced a series of awakenings that led him to seeing the world in a completely different way than most people. He began teaching others about his insight and many people followed him. After his death, his followers collected his sayings and writings and developed a tradition based on his teachings.
Conclusion
Buddhism originated in India, sometime between the 6th and 4th centuries BCE. The precise details of the founder, Siddhartha Gautama’s life, are unclear. Siddhartha was born a prince and grew up in great luxury. At 29, he left his palace and family to live as a ascetic. After six years of severe self-denial, he is said to have achieved enlightenment. He then began teaching his doctrine of suffering, rebirth, and nirvana.
There are many theories about how Buddhism originated, but the most commonly accepted story is that it was founded by Siddhartha Gautama in the 6th century BCE. Siddhartha was born into a wealthy family, but he was deeply troubled by the suffering he saw around him. He renounced his privileged life and became a monk, searching for a way to end suffering. After years of meditation, he finally achieved enlightenment and became the Buddha, or “enlightened one.” He then spent the rest of his life teaching others how to achieve enlightenment and find freedom from suffering.